Simulation technology that could prevent natural disasters is drawing market attention with recent activities of extreme weather conditions and an increase in climate change awareness. E8IGHT, a simulation-based digital twin platform company in Seoul, Korea, developed particle-based simulation software and raised the possibility of disaster prevention.
Its core software, NFLOW, is a fluid dynamics simulation software that allows the establishment of countermeasures in advance by identifying the cause and the impact of disasters such as typhoons, landslides, and flooding. NFLOW is best suited for analysing large-scale physical phenomena as it rolls over millions of particles in the simulation. It is said to be a more advanced simulation technology than mesh-based, which was commonly used in fields such as automobiles, and machinery where the simulation subject must be tightly surrounded by the grid.
E8IGHT CEO Jin Kim said, “Natural hazards can happen anytime, so we need to be prepared beforehand by using simulation and digital technology for disasters. I believe smart technology will be the key to the prevention of disasters and the safety of the public.”
NFLOW is developed by E8IGHT in-house technology, and projects particles to analyse free surface flow of complex models, structures, or a large-scale physical event such as water, air, and fine dust. It is meshless, allowing it to be operatable to even non-experts. NFLOW received level 1 GS certification authorised by Korea Testing Laboratory in 2020 March and received technical certification by ICT Tech Market and Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement in 2020 August.
NFLOW can also be equipped in E8IGHT’s simulation-based digital twin platform, NDX PRO. NDX PRO integrates and processes data such as traffic, telecommunication, service, simulation and more. It not only provides simulation results but also various digital assets in 3D through 3D visual viewer based on in-house developed high-end technology.
NFLOW in NDX PRO can continuously generate data from physical phenomena and implement to the changing data values in virtual space to analyse, predict and solve problems in the real world.

Last August, South Korea experienced the heaviest rainfall in 100 years when typhoon hit hit Gangnam District, the centre of Seoul, and caused severe flooding. Countless houses and roads were flooded due to sewage backflow causing injuries and missing people. Subway stations and other facilities also suffered tremendous damage due to the flood.
Gangnam District has a low terrain compared to nearby neighbours and is surrounded by mountains and hills, leaving it vulnerable to stagnant rainwater. This flooding disaster is said to be caused by problems of sewage pipe installation errors, lack of drainage facilities, and other factors.
POSCO, the largest steelmaker in Korea, also suffered massive flooding due to typhoon Hinnamnor striking East Asia last September. The main and core machinery was shut down for the first time in 49 years. Due to the damage, POSCO’s third-quarter operating profit this year stood at KRW900 billion (USD633 million) which was a 71 per cent decrease compared to the same period last year. POSCO announced that the typhoon was the cause of the decrease in its earnings.
According to a statistical report by Seoul Metropolitan Government, Seoul Gangnam District suffered from heavy rain for seven out of 10 years until 2020, starting with a landslide which occurred in 2011. Preparation of countermeasures for natural disasters such as heavy rain and hurricanes is not an easy feat because it is hard to predict and simulate in real-time.
Preparation of countermeasures for natural disasters such as heavy rain and hurricanes is not an easy feat because it is hard to predict and simulate in real-time. Simulation allows difficult real-world experiments and scenario planning to be carried out by duplicating a subject, system, or phenomenon in a virtual world.
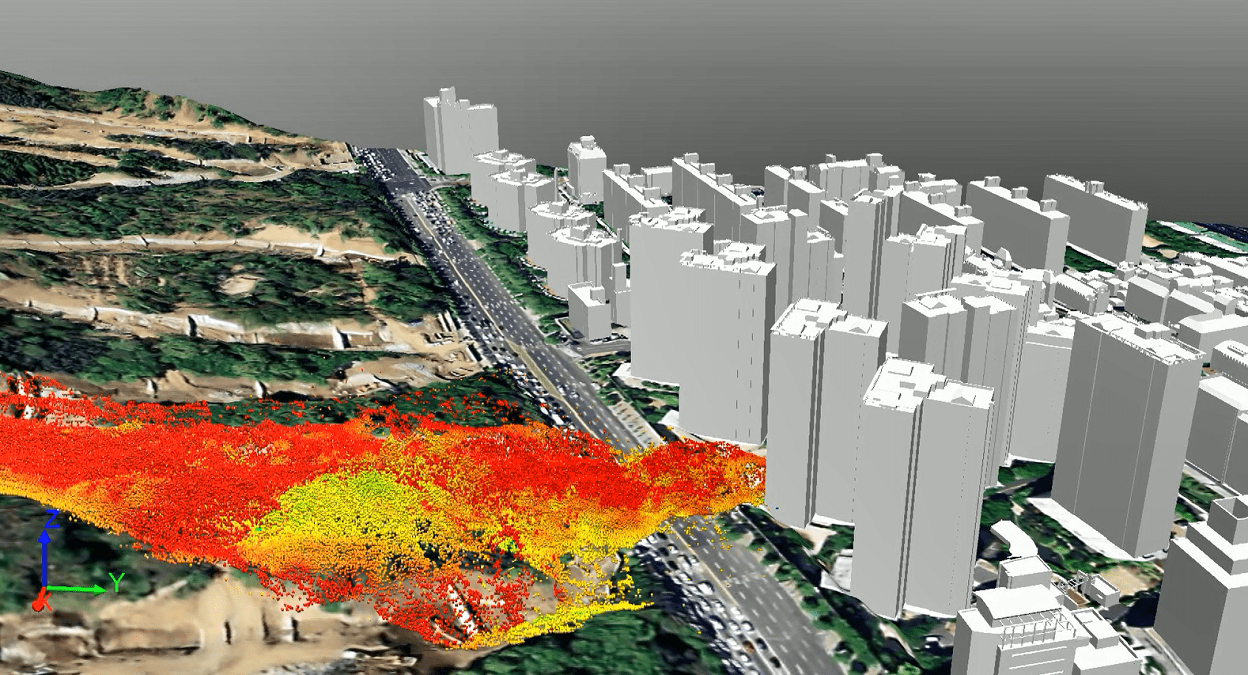

Through simulation technology, difficult scenarios could be experimented on in a virtual space to verify the hypotheses. Furthermore, it helps to set up a contingency plan, countermeasure, and more for smarter and better decisions.
E8IGHT utilises NFLOW to simulate the damage of landslides due to rain pour by analysing data on rainfall, wind direction, soil quality, and other factors. Previously, NFLOW revealed the cause of a subsea tunnel flooding accident in Korea, which occurred in the past due to a design that did not account for the inflow of rainwater.
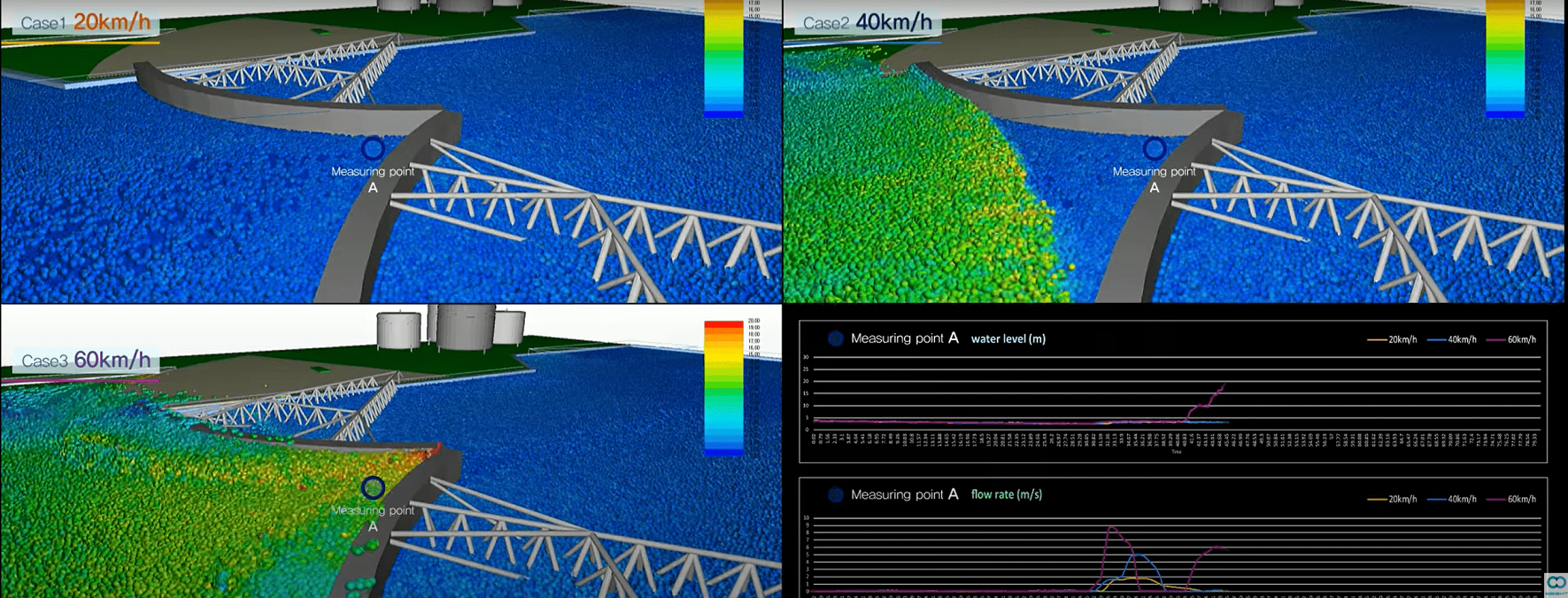
Furthermore, NFLOW also simulated Maeslantkering – a storm surge barrier on the Nieuwe Waterweg, in South Holland, Netherlands – for tsunami prevention, and successfully identified the causes of a large-scale disaster and suggested countermeasures.
Established in 2012, E8IGHT has been providing technologies through particle-based simulation and digital twin platforms that can be useful in people’s daily lives by preventing natural disasters, building smart cities and more. ![]()

